SIC | INNOVATE | RURAL
Methods and Challenges in Getting Carbon Credits In Paddy Farming
Company name
Carbon Credits In Paddy Farming
Category
Feasibility Study
Project Type
Pilot Project
Date
Oct, 2024

Executive summary
This report explores the methods and challenges in obtaining carbon credits for paddy farming, a major contributor to methane emissions, which is 86 times more potent than CO₂ over 20 years. It details sustainable farming techniques like AWD, SRI, and direct seeding that can significantly reduce methane emissions. The carbon credit system, its registration process, and India's policy stance on carbon trading and voluntary carbon markets are examined. Despite potential economic benefits, small and medium farmers face barriers to participation, due to high costs and complex verification processes. The report concludes that while carbon trading is a promising tool for emission reduction, successful implementation requires policy reforms and farmer support.
Problem statement
Traditional paddy farming practices involve prolonged flooding of fields, which suppresses weed growth but creates anaerobic conditions that promote methane production by methanogenic bacteria. This process contributes significantly to methane (CH₄) emissions, making paddy cultivation the second-largest source of methane emissions in India after livestock.
Problem statement
As India ranks third globally in methane emissions, addressing this issue is critical for mitigating climate change while ensuring sustainable rice production. The challenge lies in reducing methane emissions without compromising crop yields and farmer livelihoods, necessitating the adoption of alternative farming methods and carbon credit incentives.
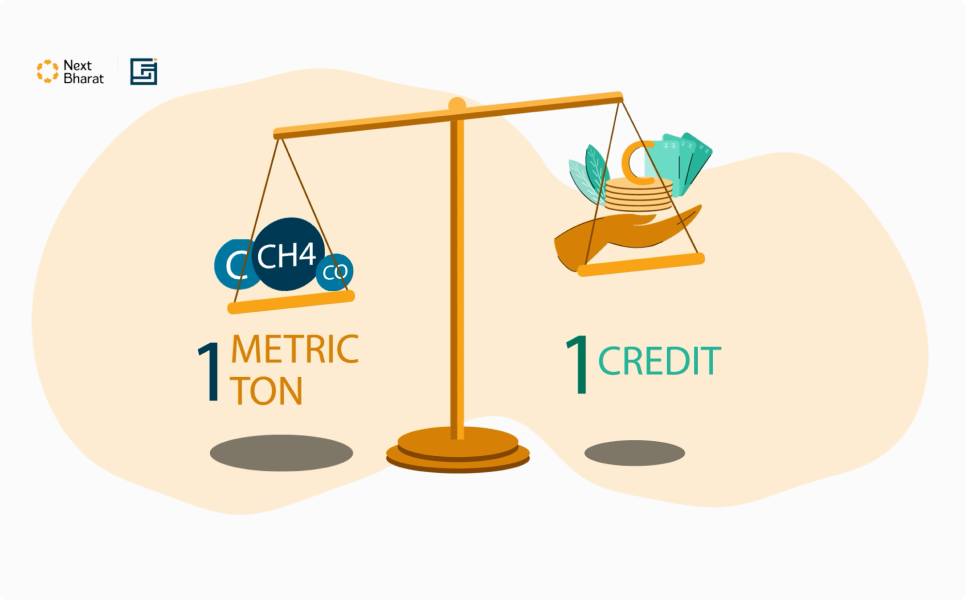
Goals and Objectives
- Assess Challenges & Methods – Identify the barriers and solutions for paddy farmers to adopt sustainable farming practices and qualify for carbon credits
- Explain Carbon Credit Mechanisms – Outline the process of acquiring carbon credits, government policies, and market dynamics in India
- Evaluate Feasibility & Implementation – Analyze the practical challenges of executing carbon trading projects in paddy farming, including financial and time constraints

Our role in execution
We are responsible for conducting research, analyzing data, and presenting insights on carbon trading and sustainable agricultural practices.
“
Efforts needed for implementation of the new methods are high and shortage of labour makes it even more expensive, given the meagre profits. ”
Farmer from Sangareddy
Learnings & Failures
Learning:
1)Importance of Methane Reduction: Paddy farming significantly contributes to methane emissions, and adopting sustainable practices can mitigate climate impact.
2)Carbon Credit Process: Understanding the steps to register, verify, and trade carbon credits, along with the challenges involved in implementation.
3)Government Initiatives & Policies: Insights into India’s stance on sustainable agriculture, voluntary carbon markets, and regulatory frameworks.
4) Barriers to Adoption: High costs, lack of awareness, and the complexity of carbon credit registration discourage small and medium-scale farmers.
Failures:
1) Pilot Project Not Executed: Due to the long execution time (around two years) and high investment requirements, the planned pilot study was not carried out.
2) Limited Practical Feasibility: Small and medium farmers struggle to benefit from carbon trading due to their limited land holdings and the high cost of required technologies.


Explore More Insights
Access the full report, related blogs, and press releases to dive deeper into the impact and execution of this project.
Empowering Success
and Well-Being
Lives Impacted
Lives Impacted
Lives Impacted
Lives Impacted





